Module 02
02.01 Comparing Different Types of Risk
Video: Understanding Investment Risk
- Risk: the uncertainty that our realized return will not be the same as our expected return
- The level of risk increases, so does the potential reward.
- The more risk you're willing to take, the more you could gain and the more you could lose.
- Risk appetite: an investor's level of comfort taking risk
- Tied to you
- Risk tolerance: how much risk that investor can take on a particular investment based on their goal and time horizon
- Tied to your individual investments
- How much risk is appropriate will depend on the combination of your risk appetite and risk tolerance.
Video: Systematic Investment Risk
- 2 broad categories of risks: systematic risk and unsystematic risk
- Systematic risk:
- non-diversifiable risk
- inescapable or unavoidable
- inherent in the stock market
- present regardless of your choice of investments
- different types of systematic risks:
- purchasing power risk: loss of purchasing power through inflation
- reinvestment risk: the risk that proceeds from an investment may have to be reinvested at a lower rate than what you had already been earning
- interest rate risk: the risk that a change in interest rate will cause the market value of a security that you own to fall
- market risk: the risk of the overall market
- exchange rate risk: the risk associated with changes in the value of currencies
- country risk or political risk: the uncertainty of returns caused by the potential of major changes in the political or economic environment of a country
Video: Unsystematic Investment Risk
- Unsystematic risk:
- diversifiable risk
- 2 types of unsystematic risks:
- business risk: the nature of a business's operation
- financial risk: credit risk or default risk - how a business finances its assets and its operations
- Diversifiable risk: the impact of these risks be reduced through diversification
Practice Assignment: Investment Risk Types
- What is risk tolerance?
- An investor’s level of comfort taking risk
- How much risk an investor can take on a particular investment based on his or her goal and time horizon
- An investor’s level of success
- None of the above
- Which of the following describes the loss of purchasing power through inflation?
- Market risk
- Interest rate risk
- Reinvestment rate risk
- Purchasing power risk
- What are the two types of unsystematic risk?
- Financial risk and business risk
- Business risk and institutional risk
- Educational risk and financial risk
- None of the above
02.02 Analyzing Investment Risk
Video: Measuring Investment Risk
- The main measures of investment risk:
- Beta: the volatility of investment relative to a benchmark
- The benchmark would often be the whole market or market index.
- Beta = 1: the investment is as volatile as the benchmark itself
- Beta < 1: the investment is less volatile than the benchmark
- Beta > 1: the investment is more volatile than the benchmark
- Standard deviation: the data dispersion relative to the average or mean value of a set of data
- Low standard deviation: more predictable investment performance
- High standard deviation: less predictable or more volatile performance
- Sharpe ratio: the risk adjusted return
- To compare the investment return to an investment that is deemed risk free, e.g., treasury bond
- To assess whether the risk is worth taking for the additional return on a particular investment
Reading: 6 Investment Risk Management Strategies
- Article: 6 Investment Risk Management Strategies
- 3 main factors of risk tolerance:
- Risk capacity: How much the investor can afford to lose without it affecting actual financial security
- Based on age, personal financial goals, and an investor’s timeline for reaching those goals.
- Need: How much these investments will have to earn to get the investor where they want to be
- A careful balancing act between taking too much risk and not taking enough
- Emotions: How the investor will react to bad news (with fear and panic? or clarity and control?), and what effect will those emotions have on investing decisions
- Hard to predict until it happens
- Risk management strategies:
- Reevaluating Portfolio Diversification and Asset Allocation
- Lowering Portfolio Volatility
- Rebalancing
- Buying bonds
- Beta
- Investing Consistently
- Getting an Investment Risk Analysis
- Requiring a Margin of Safety
- Establishing a Maximum Loss Plan
Video: Measuring Investment Returns
- Rate of return on investment: the money that's earned or could be lost on an investment
- Typically expressed as a percentage of the investment's initial cost
- e.g., If you bought a stock for $100 that grew to $110, you would have a 10% rate of return.
- Rate of return formular:
\[Return\ Rate=\frac{(Current\ Value - Initial\ Value)}{Initial\ Value} \times 100\]
Reading: What is Considered a Good Return on Investment?
- Article: What Is Considered a Good Return on Investment?
- A good return on investment is generally considered to be around 7% per year, based on the average historic return of the S&P 500 index, adjusted for inflation.
- Cash slowly loses value over time due to inflation if you don't invest.
- Putting money in a savings account that earns interest at a rate that is lower than the inflation rate guarantees that money will lose value over time.
- Different investments, such as CDs, bonds, stocks, and real estate, offer varying rates of return and levels of risk.
- It’s important to consider factors like diversification and time when investing long-term.
- Investing in stocks carries higher potential returns but also higher risk, while investments like CDs offer lower returns but are considered safer.
Practice Assignment: Assessing Investment Risk
- What is measured by beta?
- How much the return on investment is deviating from the expected or average return
- Performance, but it’s used to compare the return of an investment to that of an investment that’s deemed risk-free, like a treasury bond
- The volatility of an investment relative to a benchmark
- Data dispersion relative to the average or mean value of a set of data
- What are the three main factors of an investor’s risk tolerance?
- Risk capacity, need, and emotions
- Risk capacity, need, and wants
- Risk capacity, emotions, and logic
- None of the above
- Which of the following is the correct calculation for rate of return?
- Rate of return = [(Initial value − Current value) ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- Rate of return = [(Current value − Initial value) ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- Rate of return = [Current value ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- None of the above
- According to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), what is the national average annual percentage yield for one month of non-jumbo deposits (as of Jan 4, 2021)?
- 0.04%
- 0.05%
- 0.07%
- 0.16%
02.03 Balancing Risk and Return
Video: Investment Risk & Return
- The higher risk, the higher return
- The lower risk, the lower return
- Risk reward ratio: calculating the potential outcomes of any investment transaction - good or bad
- e.g., For a risk reward ratio of 1:3, you risk $1 to hopefully gain $3 in profits
- You divide net profits (reward), by the cost of the investment's maximum risk.
Reading: Suitability: Definition, How It's Measured, and How It's Used for Investing
- Article: Investment Risk: What Every New Investor Should Know
- Higher risk, higher potential return
- Risk balancing:
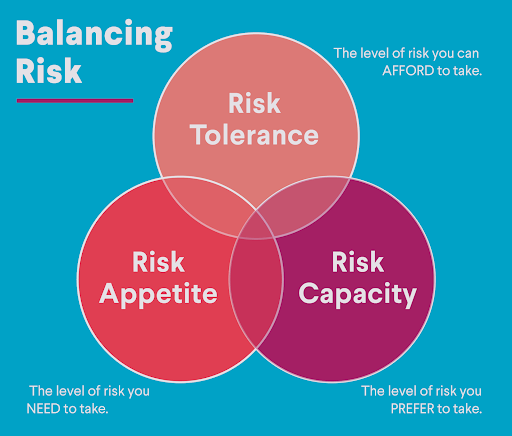
- Several types of risk:
- market
- business specific
- price volatility
- interest rate
- concentration
Video: Investment Risk Tolerance & How to Find Yours
- Risk tolerance: the amount of risk an investor is willing to take
- Risk capacity: the ability to handle risk financially
- how much can you afford to lose without affecting your security
- Risk appetite: emotional attitude about risk
Reading: Explaining the Different Types of Asset Classes
- Article: Explaining the Different Types of Asset Classes
- Different asset classes:
- Stocks (equities): a single ownership share in a publicly-traded company (a company that trades on a stock exchange)
- You can receive dividends from stocks if a company pays out part of its profits, or you might get capital gains when you sell if the price of the stock has risen.
- Bonds (fixed income): loans you make to a company or government for a predetermined amount of time at a certain amount of interest
- e.g., treasury bonds, corporate bonds, municipal bonds
- Money market accounts or cash equivalents: savings account, or certificate of deposit (CD)
- You get paid interest on the money for lending money to the financial institution.
- Real estate: buying real estate for the purposes of renting the property to generate income or to earn profits as the value of the property appreciates
- Commodities: putting money into metals, energy products, livestock, agricultural products, and so forth
- Commonly through a futures contract
- Future contract: an agreement to buy or sell a certain commodity at a specific quantity at a predetermined price at a later time
- Cryptocurrencies: investing in digital currency that is largely unregulated
- Typically dependant on a direct financial exchange between users, with no involvement from a bank or other third party
- Real estate investment trusts (REITs): investing primarily in real estate or real estate loans, traded like stocks
Practice Assignment: Risk & Return
- What is the risk-reward ratio formula?
- The cost of the investment’s maximum risk divided by net profits (which represent the reward)
- Net profits (which represent the reward) divided by the cost of the investment’s maximum risk
- Net expenses divided by the cost of the investment’s maximum risk
- None of the above
- Which of the following is NOT one of the broad categories of investment risk tolerance?
- Simple risk tolerance
- Aggressive risk tolerance
- Moderate risk tolerance
- Conservative risk tolerance
- How many different stock sectors are there?
- 5
- 7
- 11
- 15
02.04 Module Quiz
Graded Assignment: Balancing Risk and Return
- What is risk tolerance?
- An investor’s level of comfort taking risk
- How much risk an investor can take on a particular investment based on his or her goal and time horizon
- An investor’s level of success
- None of the above
- Which of the following describes the loss of purchasing power through inflation?
- Market risk
- Interest rate risk
- Reinvestment rate risk
- Purchasing power risk
- What are the two types of unsystematic risk?
- Financial risk and business risk
- Business risk and institutional risk
- Educational risk and financial risk
- None of the above
- What is measured by beta?
- How much the return on investment is deviating from the expected or average return
- Performance, but it’s used to compare the return of an investment to that of an investment that’s deemed risk-free, like a treasury bond
- The volatility of an investment relative to a benchmark
- Data dispersion relative to the average or mean value of a set of data
- Which of the following is the correct calculation for rate of return?
- Rate of return = [(Initial value − Current value) ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- Rate of return = [(Current value − Initial value) ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- Rate of return = [Current value ÷ Initial Value ] × 100
- None of the above
- What is the risk-reward ratio formula?
- The cost of the investment’s maximum risk divided by net profits (which represent the reward)
- Net profits (which represent the reward) divided by the cost of the investment’s maximum risk
- Net expenses divided by the cost of the investment’s maximum risk
- None of the above
- Which of the following is NOT one of the broad categories of investment risk tolerance?
- Simple risk tolerance
- Aggressive risk tolerance
- Moderate risk tolerance
- Conservative risk tolerance
- How many different stock sectors are there?
- 5
- 7
- 11
- 15
- Which of the following is NOT a factor of an investor’s risk tolerance?
- Market Volatility
- Risk Capacity
- Need
- Emotions
- True or False: Your money loses value if you don’t invest it.
- True
- False